How to Improve Website Speed: Proven Ways to Boost Performance
- Mike Dodgson

- Jul 19, 2025
- 16 min read
If you're wondering how to improve your website's speed, it boils down to a few core principles. You want to focus on reducing HTTP requests, getting those images compressed, and putting a Content Delivery Network (CDN) to work. Tackling these first can make a massive difference to your loading times, which helps keep visitors on your site and engaged with what you have to offer.
Why Website Performance Matters for UK Audiences

Think about it from your customer's perspective. Someone in London or Manchester clicks on your site, and the clock starts ticking. If your page takes a long time to load, their first instinct is to hit the 'back' button. That’s not just one less visitor—it’s a lost sale, a missed enquiry, or a subscriber you never gained.
The Direct Impact on Business Results
The speed of your website has a direct, measurable effect on your key business metrics. Poor performance leads to higher bounce rates, which sends a clear signal to search engines that your site isn’t delivering a great user experience. Over time, this can seriously dent your search rankings, making it that much harder for new customers to discover you.
Here are a few common scenarios I've seen:
An e-commerce shop where sluggish product pages lead to frustrated shoppers abandoning their carts.
A local service provider whose contact page lags, stopping a potential client from getting in touch.
A blog where articles load so slowly that readers give up before exploring other content.
In every one of these cases, poor performance creates a roadblock. It's a frustrating barrier that stands directly between your business and its goals. For more targeted advice, you can explore our guide on https://www.digital-sprout.co.uk/post/site-speed-optimisation-strategies-for-uk-businesses-2025.
Meeting High Expectations in the UK Market
The UK is a digitally savvy market, and with that comes high expectations. The internet infrastructure here is constantly improving. In early 2025, the median fixed broadband speed hit 123.92 Mbps—a huge leap from the previous year. With internet penetration sitting at 97.8%, you can bet that the vast majority of your audience has a fast connection and expects your website to keep up.
The high rate of mobile usage only raises the stakes. A huge chunk of your audience will be visiting your site on their phones, often while they're out and about. A fast, slick mobile experience isn't a 'nice-to-have' anymore; it's a must if you want to stay in the game. To get a handle on the full range of techniques, it's worth exploring these expert WordPress speed optimization strategies. Getting this right isn't just a technical box-ticking exercise; it’s a fundamental part of building a strong brand and hitting your financial targets.
High-Impact Fixes for Your Server and Hosting

Before you think about modifying a single image or line of code, your website's performance story has already begun. The real foundation is your server and hosting setup. Get this right, and you're building on solid ground. Get it wrong, and you'll constantly be playing catch-up, trying to fix a fundamentally slow experience.
Many businesses fall into the trap of starting with the cheapest shared hosting plan they can find. While budget-friendly, this decision often creates a major bottleneck as soon as your traffic starts to pick up.
Choosing the Right Hosting Plan
We often get caught up in on-page tweaks when trying to improve website speed, but your hosting environment is the engine room. If that engine is sputtering, no amount of polishing the exterior will make the car go faster. You generally have three main options, each with its own pros and cons.
Shared Hosting: This is where your website lives on a server alongside hundreds, sometimes thousands, of others. It’s incredibly cheap, but you're all sharing the same pool of resources. If another site on the server gets a huge traffic spike, yours can slow to a crawl. It’s really only suitable for brand-new sites with minimal traffic.
Virtual Private Server (VPS) Hosting: A fantastic middle ground. You still share a physical server, but a specific portion of its resources (like CPU and RAM) is dedicated just to you. A VPS gives you a serious boost in power and control over shared hosting, without the hefty price tag of your own machine. It's the logical next step for any growing business.
Dedicated Server Hosting: This is the top-tier option where you rent an entire physical server for your exclusive use. You get maximum power, tight security, and complete control. This is the go-to for high-traffic e-commerce stores, large-scale applications, or businesses with specific compliance and security needs.
The image above from a UK provider illustrates how these plans are typically structured, offering more resources and better performance as you move up the tiers. The key is to realistically match your website's demands with the hosting package to prevent your server from being the weak link.
A consistently slow server response time, often measured as Time to First Byte (TTFB), is a dead giveaway that your hosting is holding you back. If your TTFB is creeping over 600ms, it's a huge red flag. This metric shows how long it takes for a browser to receive the very first byte of data from your server after it makes a request.
The Importance of Server Location
Here's a simple win, especially if your customers are primarily in the UK. The physical distance data has to travel really does matter. It's a concept called latency.
If your target audience is in Leeds but your server is in Texas, every request and every piece of data has to make a transatlantic journey. By simply choosing a host with a UK-based data centre, you can drastically cut down that travel time. This one change can shave precious milliseconds off your load time for every single UK visitor.
Server-Side Technologies That Matter
Beyond the physical hardware, modern server-side technologies can give your site a serious performance injection. These are often settings your hosting provider can help you enable, and they make a real-world difference.
Update Your PHP Version: If your website is built on a platform like WordPress, it runs on the PHP programming language. Using an old version isn't just a security risk; it’s a performance killer. Simply updating to the latest stable version of PHP can make your entire site run more efficiently.
Implement HTTP/3: This is the newest version of the protocol that sends data across the web. It was designed from the ground up for speed, allowing browsers to download multiple files at once over a single connection—a massive improvement over older protocols.
Enable Compression: Think of this like zipping a folder before you email it. Technologies like Gzip or Brotli compress your site's files (HTML, CSS, JavaScript) on the server before sending them. The visitor's browser quickly unzips them upon arrival. Smaller file transfers mean faster load times. It's a must-have.
If you're running WordPress and want to get really deep into the technical side, there's a great guide on mastering WordPress server configuration. Getting these server-level fixes in place is important because they provide a speed boost to every single person visiting every single page on your site.
Managing Your Images and Media Files
Visual content is fantastic for grabbing your audience's attention, but it's often the single biggest culprit behind a slow website. Think of large, uncompressed images and videos as heavy luggage your visitor’s browser has to download before anything useful appears on screen. Every banner, product shot, and embedded video adds to the total page weight, so getting this under control is one of the most effective ways to speed things up.
The root of the problem? Many businesses upload high-resolution images straight from a professional camera or a stock photo site. These files can easily be several megabytes in size when, in reality, a fraction of that is all you need for a sharp, crisp display online.
Switch to Modern Image Formats
For years, we've relied on JPEG and PNG for web images. While they still have their uses, modern formats like WebP and AVIF offer a much better deal, striking a perfect balance between visual quality and file size. We're often talking about significant reductions in file weight with no noticeable drop in clarity.
Here's a quick rundown:
WebP: Developed by Google, WebP has become a brilliant all-rounder. It can produce images that are typically 25-35% smaller than an equivalent JPEG while looking just as good. It also supports transparency like a PNG, but at a much smaller file size. Browser support is now nearly universal, making it a safe and very smart choice.
AVIF: This is the new kid on the block, and it offers even more impressive compression. An AVIF file can be around 50% smaller than a similar JPEG. The only catch is that its browser support isn't quite as widespread as WebP just yet, and creating AVIF files can be a bit more intensive. It's a fantastic option when you need maximum compression, but you'll want to have a WebP or JPEG fallback ready for older browsers.
To help you decide, here’s a quick comparison of these modern formats.
Modern Image Format Comparison
This table compares modern image formats to help you choose the best one for different use cases on your website.
Format | Best For | Key Feature | Typical Size Reduction |
|---|---|---|---|
WebP | All-purpose web images (photos, graphics) | Excellent balance of quality & size; supports transparency | 25-35% vs JPEG |
AVIF | High-quality photos where size is critical | Superior compression; supports HDR | ~50% vs JPEG |
SVG | Logos, icons, and simple illustrations | Vector-based, scales infinitely without losing quality | N/A (often smallest) |
PNG | Graphics needing high-quality transparency | Lossless compression, sharp edges | Larger than WebP |
Choosing the right format is a huge step towards a faster site. For more on this topic, you can explore our guide on image optimisation techniques for business growth.
Always Compress Images Before Uploading
Picking the right format is only half the story. You also must compress your images to shrink their file size. This process intelligently strips out unnecessary data from the image file without messing with how it looks to the naked eye. You've got a couple of ways to tackle this.
You can use brilliant online tools like TinyPNG or Squoosh. These web-based services let you upload your images, apply compression, and then download the much smaller file to pop onto your site. It’s a simple manual step, but it makes a world of difference.
If you're on a platform like WordPress, you can lean on plugins that automatically compress images the moment you upload them. This is a great "set it and forget it" approach that saves you time and ensures every single image is modified for speed.
From my experience, a good rule of thumb is to get most of your website images well under 100KB. For those big, full-width hero images, you might aim for under 250KB. Sticking to these targets is a really practical way to build a faster website.
The infographic below shows the direct benefit of these kinds of performance techniques. It illustrates how caching—a similar method for serving files more efficiently—slashes page load times.
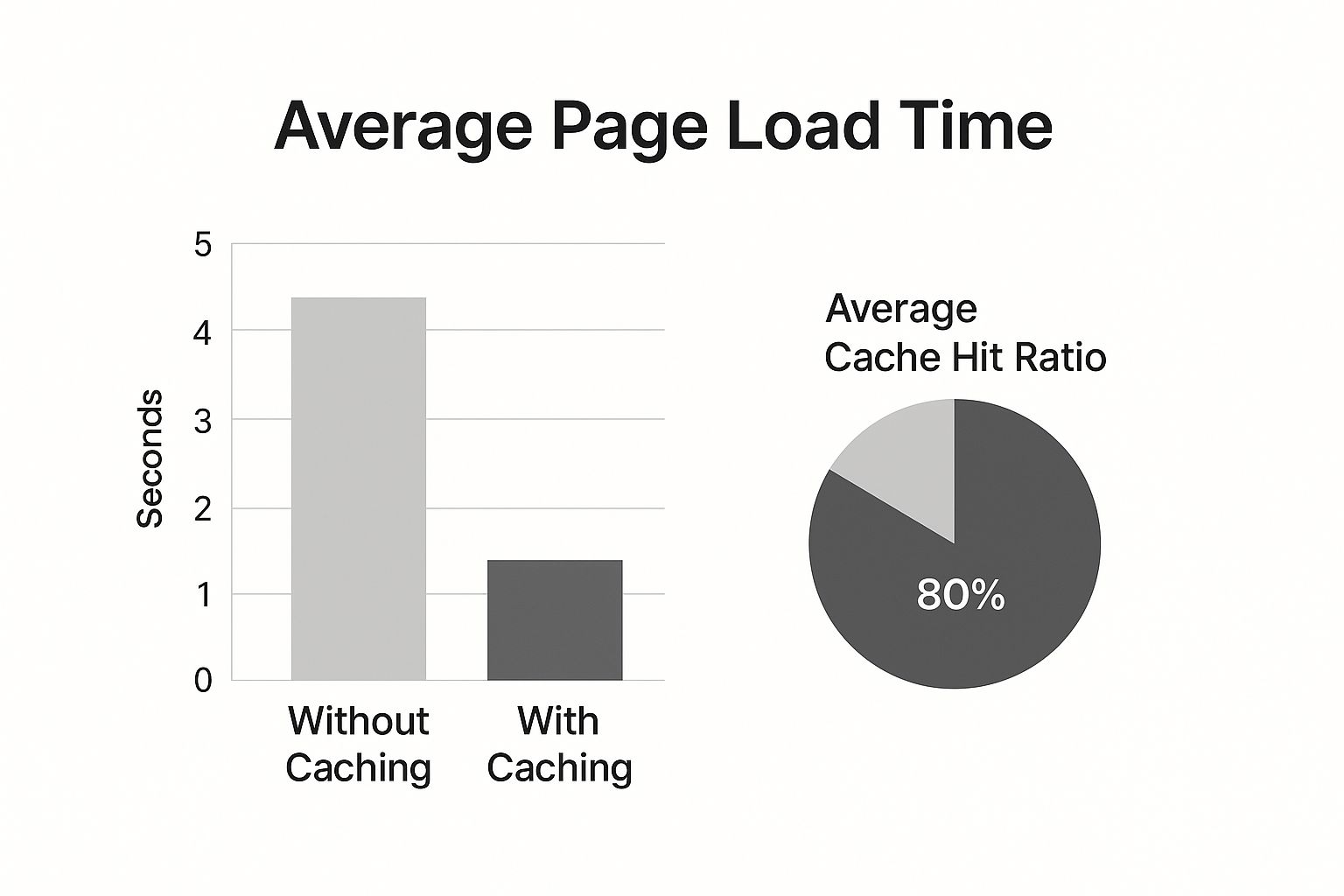
The data speaks for itself. Implementing simple performance measures leads directly to big wins in speed and efficiency.
Handle Your Video Content Smartly
If images are heavy luggage, video is a shipping container. A single video file can easily be larger than all the other elements on your page combined. Because of this, you should never host video files on your own server. It will absolutely drain your bandwidth and bring your site to a grinding halt for anyone trying to visit.
Instead, always upload your videos to a dedicated platform like YouTube or Vimeo. This offloads all the heavy lifting to their incredibly powerful, globally distributed servers. You can then simply embed the video on your page using the iframe code they provide.
To take it a step further, make sure you lazy load your video iframes. By default, a browser starts downloading an embedded YouTube video the moment the page loads, even if the visitor never scrolls down to it or clicks play. Lazy loading stops this. It tells the browser to only load the video player when the user actually scrolls it into view. This one simple trick can dramatically speed up the initial load time for any page with a video on it.
Tidying Up Your Code and Scripts for a Faster Site
You’ve sorted out your server and squashed your images down to size. That’s a brilliant start. But even with all that in place, messy, inefficient code can completely undo your hard work and leave your site feeling sluggish.
Every line of code, every script you add, and every disorganised file forces a visitor’s browser to work harder just to show your page. This digital baggage tends to build up over time—a new feature here, a plugin for a one-off campaign there, an embedded social media feed. Each one adds its own weight, gradually slowing things down. A proper code clean-up is one of the most direct ways to build a snappier, more responsive website.
Minify and Combine Your Code
Think of your website's code—the HTML, CSS, and JavaScript—as instruction manuals for a browser. As you build and tweak your site, these manuals get filled with comments, notes, and extra spacing that help developers keep track of things. That's great for humans, but for a browser, it's just clutter.
This is where minification comes in. It’s the process of automatically stripping out everything the browser doesn’t need to actually run the code, like:
White space and line breaks
Code comments
Unnecessary delimiters
You end up with a much smaller, leaner file that does exactly the same job but downloads a whole lot faster.
Beyond just minifying, you should also be combining files. Every time a browser needs a separate CSS or JavaScript file, it has to make a new request to your server. By bundling multiple files into one—a process called concatenation—you can slash the number of requests needed. It’s a huge win for performance.
I’ve seen themes that call ten different CSS files. By combining them all into a single, minified file, the browser only has to make one request instead of ten. It might sound like a small change, but those saved requests add up incredibly fast.
Defer JavaScript That Isn't Immediately Needed
Not all scripts need to load the second someone lands on your page. Some are required for displaying the basic layout, but many others—like pop-up chat boxes, social sharing buttons, or certain analytics trackers—can wait.
By default, when a browser hits a tag in your HTML, it stops everything to download and run it. This is known as "render-blocking" because it literally blocks the rest of your page from appearing.
You can get around this by deferring any non-critical JavaScript. All it takes is adding the attribute to the script tag. This simple instruction tells the browser, "Go ahead and download this in the background, but don't stop rendering the important stuff." The script only runs once the main page content has loaded, making the site feel significantly faster to your visitors.
Do a Regular Audit of Third-Party Scripts
Third-party scripts are one of the most common culprits behind a slow website. These are the snippets of code you pull in from other services to add functionality. We're talking about things like:
Google Analytics for tracking visitors
Advertising network scripts
The Facebook Pixel for remarketing
Customer support chat widgets
Embedded social media feeds from Twitter or Instagram
While these tools are often invaluable, they carry a performance tax. Each script adds a request to an external server you don't control. If their server is having a slow day, your website will be slow too.
It is a good practice to regularly audit these scripts. Go through your site and ask yourself honestly: do we really still need this? If a script from an old marketing campaign is still loading on every single page, get rid of it. For the scripts you keep, see if there are lighter, more efficient versions available. These clean-ups are a core part of a wider strategy, which you can learn more about in our guide on what is technical optimisation.
Keeping your site fast is especially important for engaging UK users. Recent data reveals that UK mobile sites take an average of 1.8 seconds for the main content to load. And with 66.02% of all UK web traffic now coming from mobile, every millisecond you shave off helps keep users happy and on your site. For more on this, check out the full website statistics report from Reboot Online. The small code adjustments we’ve covered here can make a real difference to those loading times.
Using Caching and a Content Delivery Network

When it comes to making a website noticeably faster, two of the most effective tools in your arsenal are caching and a Content Delivery Network (CDN). Think of them as a powerful duo working together to lighten the load on your server and your visitor’s browser.
The image from Cloudflare above paints a clear picture of how a CDN shortens the distance between your website and your users. By storing copies of your site's files on servers around the globe, it physically brings your content closer to your audience, slashing the latency that slows things down.
Demystifying Browser Caching
Picture this: a visitor lands on your website for the very first time. Their browser has to download every single element from scratch – your logo, stylesheets (CSS), interactive scripts (JavaScript), and all the images. That takes time.
Browser caching is simply a smart instruction you give to that visitor's browser. It says, "Hey, you've already got these files. Just keep a copy handy, and next time you stop by, you won't have to download them all over again."
So when that user returns, their browser grabs static files like your logo and CSS straight from its local memory. The result? A near-instant page load. It's a massive win for user experience, especially for your loyal, repeat visitors. If you're using WordPress, it’s worth exploring how WordPress caching works to really get a grip on serving content faster.
How a Content Delivery Network Works
While browser caching is great for repeat visitors, a Content Delivery Network (CDN) benefits everyone, especially on their first visit. A CDN is a global network of servers that keeps copies of your website's static assets, like images, CSS, and JavaScript.
Let’s say your website is hosted on a server in London. When someone from Glasgow tries to access it, their request doesn't have to travel all the way down to London and back. Instead, a CDN serves the files from the closest server in its network—perhaps one in Manchester or even Glasgow itself.
By drastically shortening the physical distance data needs to travel, a CDN can slash load times. It’s like having a local branch of your website in dozens of cities around the world, ensuring fast delivery for every user. This is a fundamental part of modern web performance.
For any business with a UK audience, it is a good idea to choose a CDN with plenty of Points of Presence (PoPs) across the UK and Europe. Providers like Cloudflare, Bunny CDN, or Fastly have extensive networks in the region, which is key to delivering a consistently snappy experience to your local customers.
Why These Methods Are So Effective
Putting caching and a CDN in place effectively moves the heavy lifting away from your single web server. It distributes the workload, making your site far more resilient to traffic spikes and faster for users no matter where they are. This isn't just a minor tweak; it's a foundational change that tackles core performance bottlenecks head-on.
These strategies are incredibly relevant when you look at performance across different UK sectors. A 2025 analysis showed huge speed gaps between industries. The fashion sector, for instance, where 37% of consumers shop mostly online, had a surprisingly poor average speed score. Their sites registered a high interaction delay of 321 milliseconds—well above the sub-200ms recommendation. By comparison, charity websites performed much better on layout stability, proving that a one-size-fits-all approach just doesn't cut it.
Combining caching with a CDN is a cornerstone of a high-performing website. These methods work in tandem to cut latency and server load, which directly translates to a faster, more reliable experience for every single visitor. To see how this fits into the bigger picture, check out our technical SEO basics 2025 guide for business owners.
Answering Your Top Questions About Site Speed
Even with the best plan, you're bound to have questions as you start digging into your website's performance. It’s a common part of the process. Let’s tackle some of the most frequent queries I hear, giving you straightforward answers to guide you through the final stages. We'll cover the real impact on SEO, how to get reliable speed data, and what targets are actually worth aiming for.
Does Website Speed Really Affect SEO Rankings?
Yes, it absolutely does. This isn't just a theory; Google has been clear for years that site speed is a ranking signal for both desktop and mobile searches. Think about it from their perspective: a faster website creates a better user experience, and user experience is at the core of their entire ranking philosophy.
When your site loads in a snap, people tend to stick around, read your content, and are more likely to become customers. All of these behaviours—low bounce rates, longer time on page—send strong, positive signals to search engines. It tells them your site is valuable. On the flip side, slow sites are frustrating. They make people leave, which, over time, can really damage your rankings.
While speed is just one piece of the puzzle, its impact is huge. A fast site doesn't just make Google's bots happy; it improves every other metric you care about, from engagement right through to sales. It's the foundation of great SEO.
How Can I Accurately Test My Website's Speed?
Testing your site's speed isn't about mashing the refresh button and timing it with a stopwatch. To get a true picture, you need objective data from proper tools that can show you where the real bottlenecks are hiding. Using a couple of different tools is usually the best approach, as they each offer a slightly different perspective.
Here are three of the best free tools I recommend to everyone:
[Google PageSpeed Insights](https://pagespeed.web.dev/): This should be your first stop. It gives you a performance score from 0-100 for mobile and desktop, and provides a tailored list of recommendations based on Google's own Core Web Vitals.
GTmetrix: This tool is fantastic for getting into the nitty-gritty. It generates a 'waterfall' chart, which is a visual breakdown of every single file your site loads. It's the best way to pinpoint exactly which images, scripts, or fonts are causing delays.
WebPageTest: For a truly detailed analysis, WebPageTest is the gold standard. It lets you test from different locations across the globe, on real browsers, and even simulate different internet connection speeds. This gives you invaluable insight into how people with slower connections actually experience your website.
When you're running these tests, don't get hung up on the overall score. Instead, pay close attention to the Core Web Vitals: Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), Interaction to Next Paint (INP), and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS). These user-focused metrics are what Google really cares about.
What Is a Good Website Speed to Aim For?
Honestly, chasing a perfect 100/100 score on every tool can send you down a rabbit hole. The real goal should be to deliver a great experience for your actual users. You want your site to feel fast and responsive.
A solid benchmark to aim for is a load time of under 3 seconds. Study after study shows that this is the point where people's patience really starts to wear thin. If you can get your key content visible and interactive within that window, you're doing well.
For more specific goals, focus on hitting Google's recommended targets for the Core Web Vitals:
Metric | Target | What It Measures |
|---|---|---|
Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) | Under 2.5 seconds | How long it takes for the main content (like a banner image or text block) to appear. |
Interaction to Next Paint (INP) | Under 200 milliseconds | How quickly your page reacts when someone clicks, taps, or types. |
Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) | Below 0.1 | How visually stable your page is. A low score means elements don't annoyingly jump around as the page loads. |
If you can hit these targets, you can be confident you're providing a strong user experience. And remember, with mobile traffic dominating here in the UK, it’s a good idea to have your mobile performance up to scratch. A fast, reliable experience for every single visitor is one of the most powerful things you can do for your business.
At Digital Sprout, we specialise in the technical details that drive real growth. If you want to turn your website into a high-performing asset that attracts and converts customers, explore our Technical Optimisation service today.
.jpg)